According to the prevailing laws in different countries, both new and existing buildings, it is mandatory to provide adequate fire protection to the occupants.
Common windows which are widely in use in architectural applications, they do not satisfy this requirement. The glass panes are broken when the surface temperature differences are over than 40°C. Also usual type of laminated safety glass has a similar behavior and it cannot be considered safe in case of fire. Finally, securit type of safety glass, although it is significantly more resistant to temperature changes (it can withstand temperatures up to 350°C), however, it is insufficient in fire conditions where temperatures reach the 1000°C.
This demand is being fulfilled by “fire-resistant glazing” which stand for a predetermined time at a temperature of around 1000°C, in order to ensure adequate escape time for occupants in case of fire.
These glass panes are in various types such as simple with wired reinforcement, monolithic, laminated with intermediate heat activated blowing material.
According to the behavior and performance, these glasses are divided to meet the fire safety requirements of all categories:
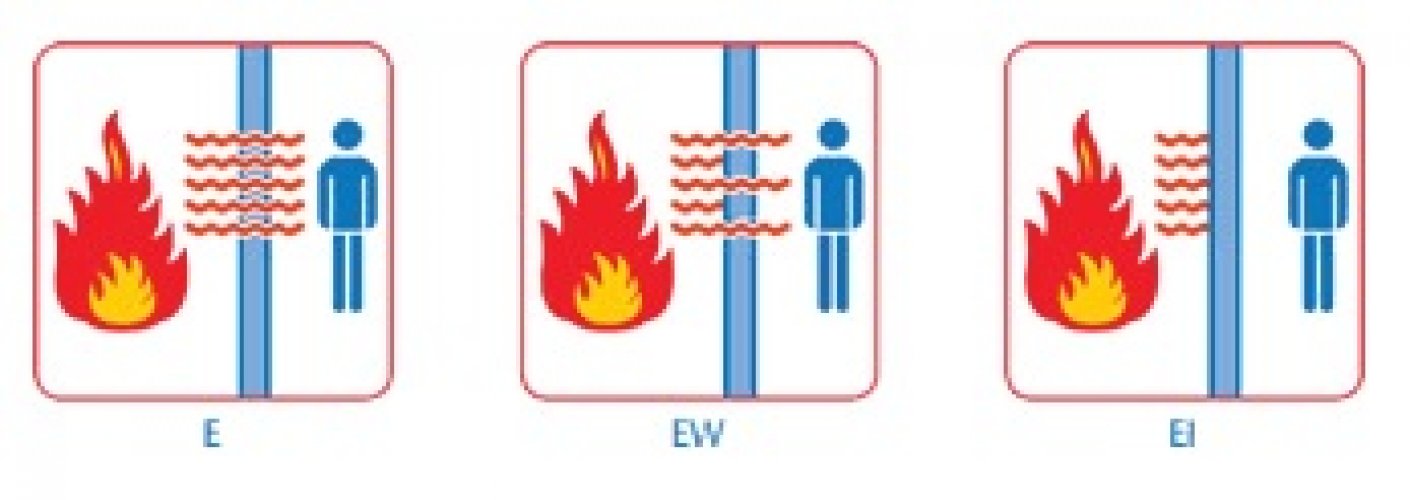
INTEGRITY (INTEGRITY CLASS E):
The glass must remain impenetrable by flames, smoke and fumes. The flame appearance is not allowed in the locked side for specific default time.
INSULATION (INSULATION, CLASS I):
The glass panes of this class prevent the temperature rise above 140°C average on the locked side and in any case the temperature should not to exceed 180°C at any point for a predetermined time.
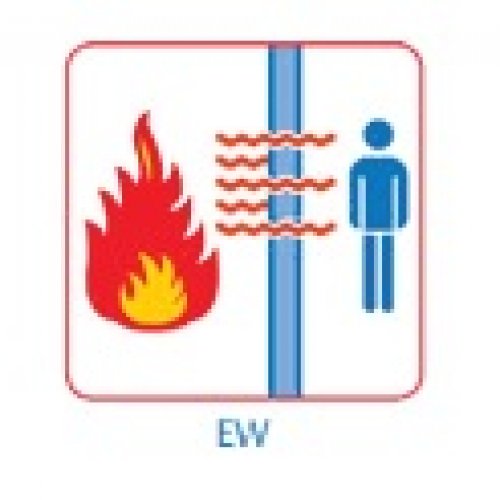
RADIATION (RADIATION, CLASS W):
The glass panes of this class, reduce the possibility of transmission of fire as a result of radiant heat, either throw of the glass pane itself, or from the unexposed side in objects that are near the glass pane.
- Public buildings
- Hotels
- Gas stations
- Schools
- Hospitals
- Restaurants
- Residences